The rubber injection molding process delivers uncured elastomer into a sealed, heated cavity under high pressure, which excludes manual loading and assures uniform material flow for different shapes. It assists in precise temperature profiling and automated mixing so each part cures tight tolerances and repeatable mechanical properties.
Unlike older compression or transfer methods, it lowers scrap and cycle times and supports higher-volume output. It also has complex gating designs and instantaneous monitoring, which renders production more predictable.

Table of Contents
ToggleHow Rubber Injection Molding Works
The rubber material is first heated and plasticized in a barrel under controlled temperature and pressure in the rubber injection molding process. Then, it is injected into a closed mold cavity. That’s where it vulcanizes. Engineers fine-tune shot volume and injection speed to address runner geometry and part shrinkage. The tight control lowers flash and assures a precise, stable cure.
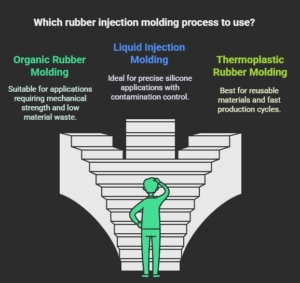
Organic Rubber Injection Molding
This rubber injection molding process uses nitrile, EPDM, or natural rubber. Engineers pre-heat these compounds to decrease viscosity during injection; it demands tight thermal control to avoid premature crosslinking. Gating systems must handle higher friction and scorching, so molds have complex venting channels. This process contributes to reliable mechanical strength and low material waste.
Liquid Injection Molding
Such rubber injection molding process involves liquid silicone rubber that cures through a platinum-catalyzed reaction. The two-component system must be mixed with precision. The injection pressure must be monitored to circumvent air entrapment. Many manufacturers use static mixers and cold-runner technology to keep the uncured silicone at low temperatures until it enters the heated mold. It averts contamination and preserves a steady shore hardness.
Thermoplastic Rubber Injection
Thermoplastic elastomers like TPE and TPR do not undergo chemical crosslinking in this rubber injection molding process. Instead, they melt and flow under heat and then solidify once cooled. It allows the leftover material to be reused. Some thermoplastic formulations demand fast cycle times and higher injection velocities. Hence, molds might incorporate efficient cooling channels. The result is a repeatable process with excellent dimensional stability and less material discarded.
Key Advantages of Rubber Injection Molding
Compared with the traditional molding process, rubber injection molding is becoming the new standard in the industry due to its unique technological advantages, mainly reflected in the following aspects.
Higher Efficiency and Reduced Cycle Times
Injection presses use controlled barrel temperatures and rapid-fill gating to cut cure times. It lets rubber compounds flow fast into heated molds to lower each cycle by several seconds. For example, a LIM system may compress a 90-second cure to 45 seconds with uniform vulcanization.
Improved Precision and Consistency
Servo-driven injection units and closed-loop feedback systems guarantee exact shot sizes and stable melt flows. Such a setup tightens part tolerances down to microns. Apart from that, real-time monitoring of mold cavity pressure also helps perceive minute variances before defects accelerate.
Greater Material Utilization and Waste Reduction
Hot-runner molds and direct gating diminish scrap. Less flash and more precise shutoff lines cut material loss. Many operations regrind and reintroduce non-vulcanized offshoots to slash raw material use.
Automation Integration for Increased Scalability
Robotic arms remove parts and place inserts, which helps eradicate manual handling and contamination. Automated part inspection with infrared or laser sensors provides inline quality checks. Such integrated work cells empower facilities to scale production fast without harming repeatability.
Common Applications in Different Industries
Rubber injection molding technology, with its high precision and flexible adaptability, has been widely used in the manufacture of key components in the automotive, medical, and industrial fields.
Automotive Seals, Gaskets, and Dampeners
Important automotive components, such as seals, gaskets, and dampeners, face intense thermal cycling, chemical exposure, and high friction. FKM and HNBR compounds are common due to their oil and heat resistance. Cavity pressure control optimizes vulcanization and molecular alignment.
The rubber injection molding process warrants repeatable geometry and unchanging material distribution in multifaceted part shapes. Specialized hot-runner systems also help exclude scrap with exact shot volumes. Resulting components tolerate exciting under-hood temperatures and protracted service intervals without losing elasticity.

Medical Silicone Components for Devices
Medical silicone components demand biocompatibility, low extractables, and stable mechanical properties under sterilization. Medical-grade LSR needs ultra-clean tooling and maintained cure profiles. Any residual catalyst or crosslinker can jeopardize device safety.
The rubber injection molding process diminishes contamination risk while confining material flow within enclosed channels. Temperature and flow monitoring helps inhibit air entrapment and guarantees steady durometer levels. That control is key to long-term reliability in catheters, seals, or implantable devices.
Industrial O-rings, Gaskets, and Vibration Isolators
They must tackle aggressive fluids, stress, and temperature fluxes. Engineered rubber compounds, including fluoro silicone or EPDM injection molding, offer abrasion resistance and chemical durability. Tools incorporate multiple gates to manage large-part designs and thwart knit lines.
The rubber injection molding process simplifies producing convoluted profiles while metering material flow. Automated degating systems trim excess flash and lessen manual finishing. High-precision O-rings and dampeners keep rotating machinery sealed and stable under heavy loads.
Dekuma: Reliable Partner for Rubber Injection Molding Machines
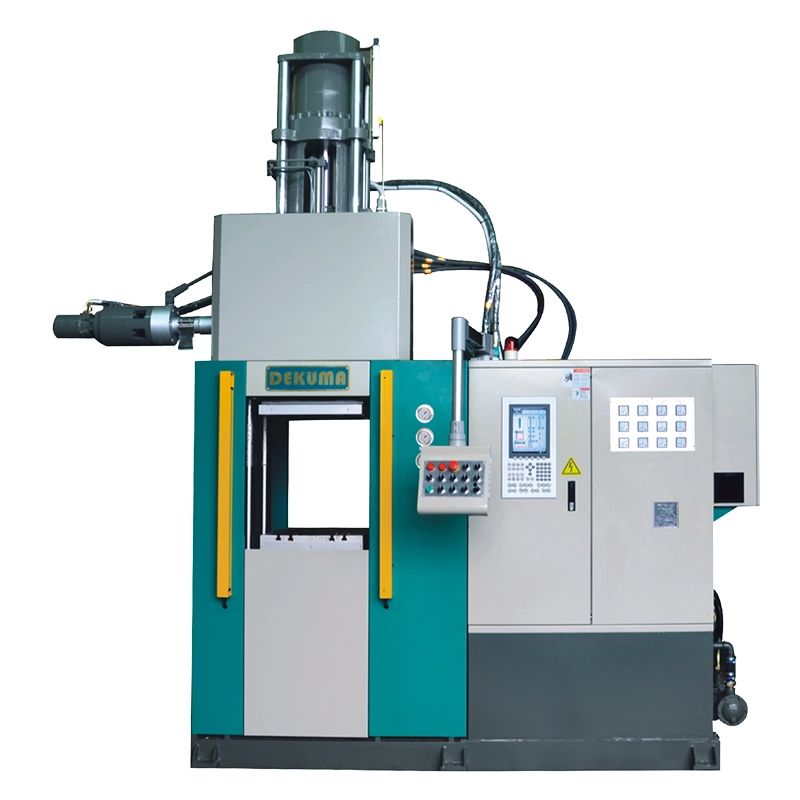
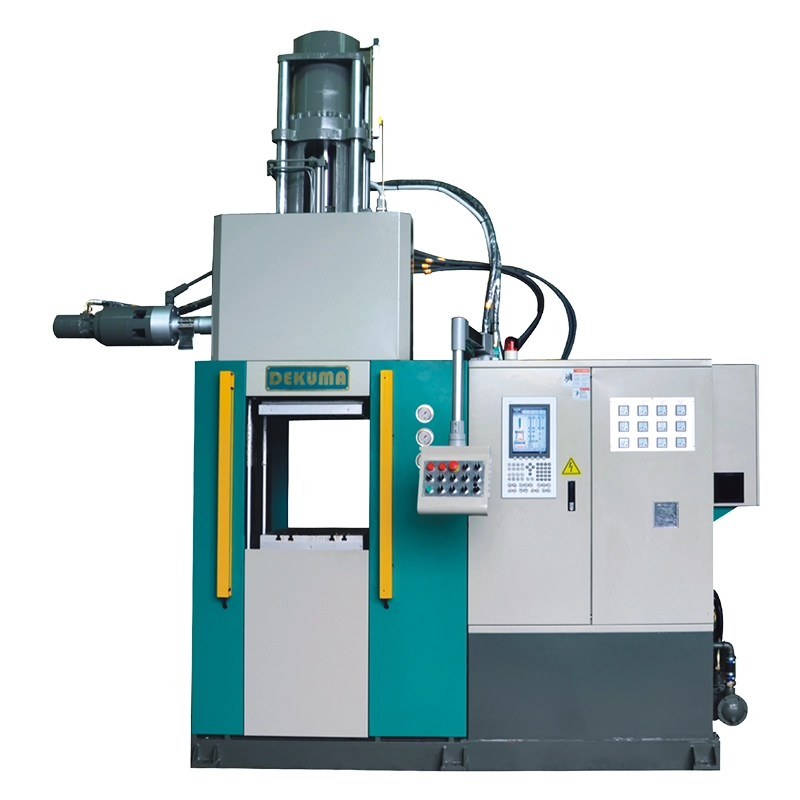
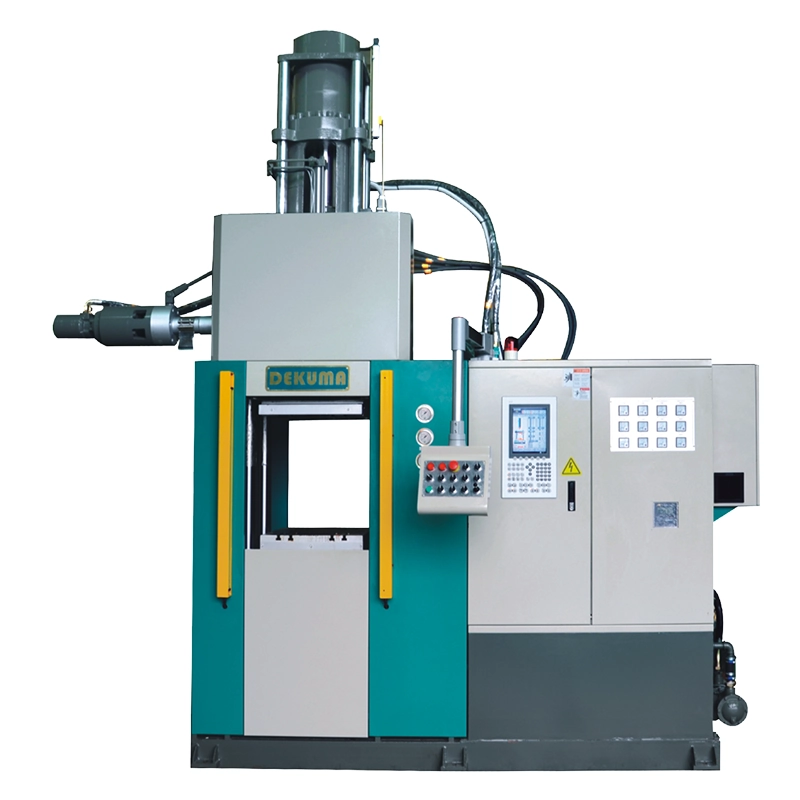
As a trusted manufacturer of rubber injection molding machines, Dekuma serves customers around the world with high-precision and high-reliability equipment solutions. Our flagship products, the RV series rubber injection molding machines, deliver dependable performance for your production needs:
- Energy efficiency: Imported double-layer insulating plates reduce energy consumption by 40% and ensure the stability of the hydraulic system.
- High precision: Injection and clamping strokes are controlled by world-renowned electronic scales, achieving a precision of 0.05%.
- Wide application: Dekuma RV rubber injection molding machines are widely used in automotive, electrical, and general industrial applications to produce parts such as rubber vibration isolators, seals, cable connectors, and pipe connectors.
Dekuma will showcase the RV300F and RV200F rubber injection molding machines at CHINAPLAS 2025 from April 15-18, 2025. Welcome to visit Booth 8B41 to explore how our equipment helps you with high-precision rubber molding!

Conclusion
Rubber injection molding realizes high-precision and low-waste production of complex parts across automotive, medical, and electronic industries. A quality rubber injection molding machine, like Dekuma RV300F and RV200F, can help you achieve optimal results. Visit us at CHINAPLAS 2025 (Booth 8B41) or explore more on our website.




