- Yinzhu Road, Zhouwu Industrial Park, Dongcheng District, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China.
- Email:info-rim@dekuma.com
- Tel: +86-769-22667207
- Mobile: +86-15622909600
From natural rubber to silicone and EPDM, discover how Dekuma machines adapt to the unique properties of each material — ensuring optimal flow, material integrity, and cycle efficiency.
Rubber types vary in molding parameters and product performance. For example, natural rubber offers good elasticity but lacks oil resistance, while nitrile rubber is oil-resistant at the expense of flexibility.
Choosing the right type of rubber optimizes molding conditions and achieves the desired product characteristics.
Besides, it is equally important to ensure the rubber injection molding machine is compatible with the specific characteristics of the rubber material. Each rubber has distinct requirements for injection pressure, clamping force, and temperature control.
A well-suited machine ensures precise alignment with these requirements, contributing to consistent product quality and reliable performance.
Determined by molecular weight and structure, it affects flowability, mold filling speed, and consistency.
Higher viscosity and molecular forces demand greater pressure for effective mold filling and material flow.
Dependent on thermal stability and curing behavior, unstable materials require lower processing temperatures.
Influenced by thermal conductivity and part thickness, lower conductivity or thicker parts cool slower.
Material | Natural rubber | EPDM | Silicon rubber | Thermoplastic elastomers |
Features |
|
|
|
|
Application |
|
|
|
|
Injection molding requirements |
|
|
|
|
For silicone rubber injection molding, Dekuma offers a reliable solution tailored to high-precision and hygiene-critical applications, including electronics and infant care.
Engineered for thermoplastic elastomers, such as TPE injection molding, Dekuma RV-SE series machines offer stable, repeatable results in automotive applications.
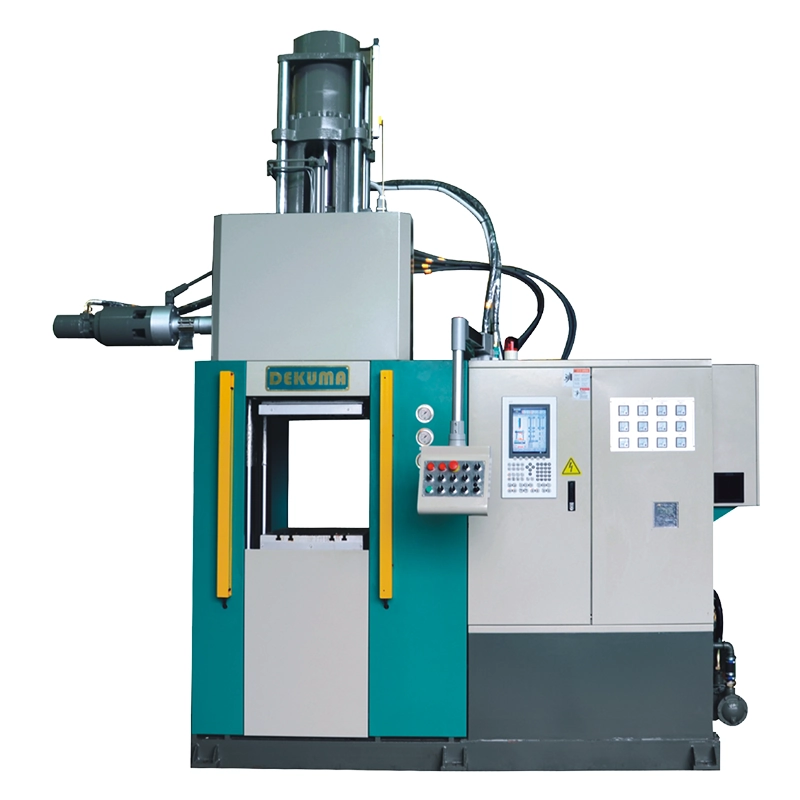
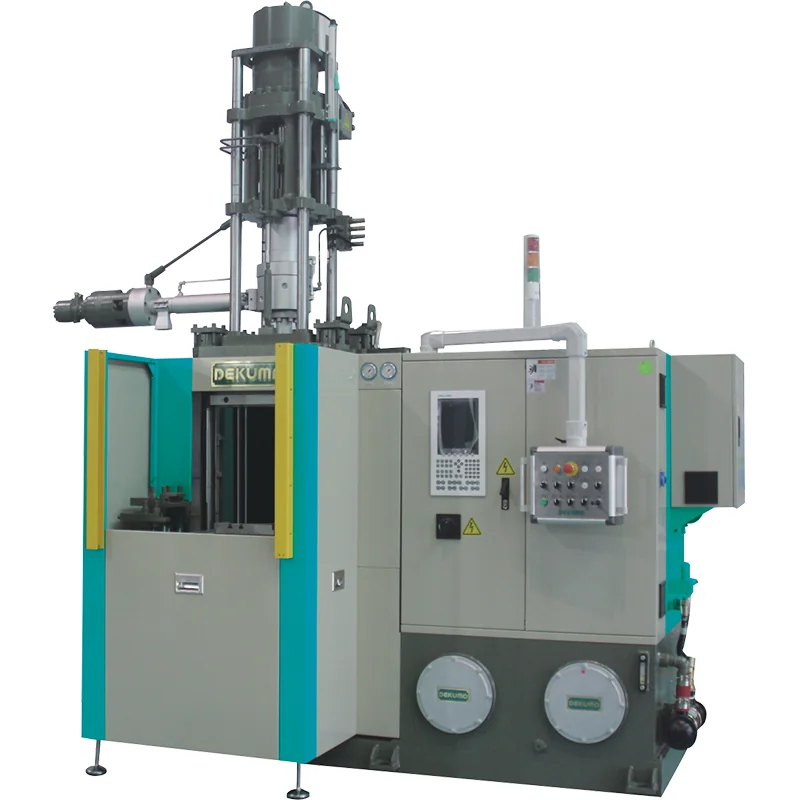


Dekuma RV-series machines are tailored for EPDM and natural rubber injection molding, widely used in automotive, power, and civil industries.
Ideal for silicone rubber and EPDM injection molding, Dekuma RA-series machines deliver exceptional performance in high-voltage composite insulator production.
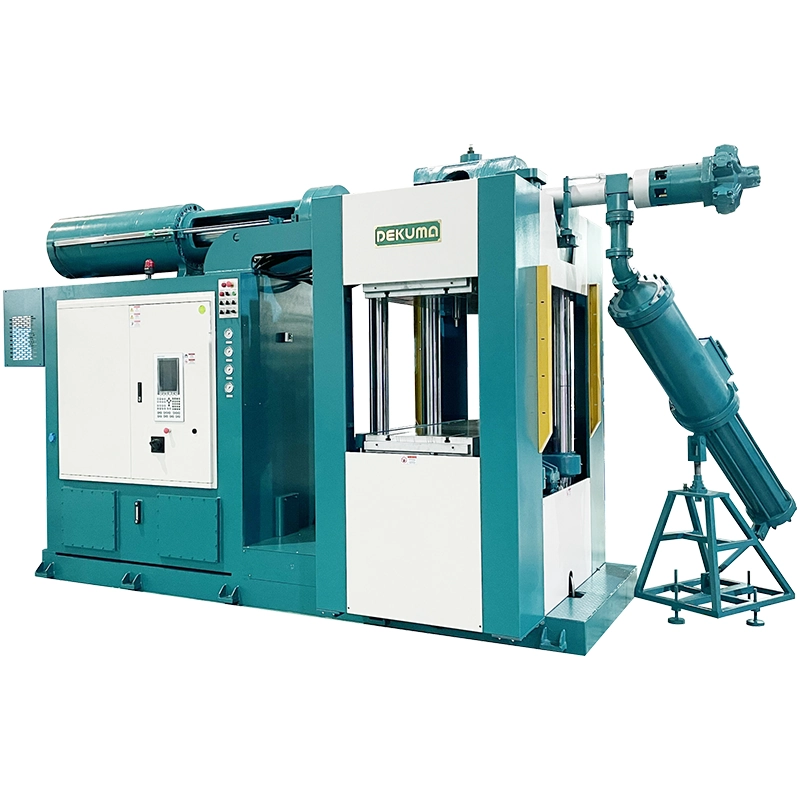


Yes, a single machine and mold can process various rubber types—such as NR, EPDM, or silicone. However, key parameters, including temperature, pressure, and injection speed, must be adjusted based on the material’s properties.
Nitrile rubber (NBR) and EPDM are commonly used in automotive sealing applications.
NBR has good oil, abrasion, and aging resistance and is suitable for sealing automotive parts that come into contact with oil, while EPDM features excellent aging, ozone, and corrosion resistance and is suitable for protective seals in automobiles.
The cycle time for the rubber injection molding varies depending on factors such as material, product complexity, and machine performance and typically ranges from a few tens of seconds to a few minutes.
Compared to compression molding, rubber injection molding offers precise results and consistent quality. It can create parts with complex shapes, provides good strength, and is suitable for producing large quantities with little need for extra finishing.
Yes, EPDM can be injection molded effectively due to its good flowability and thermal stability. EPDM injection molding is suitable for producing complex seals, gaskets, and insulation parts in various industries.